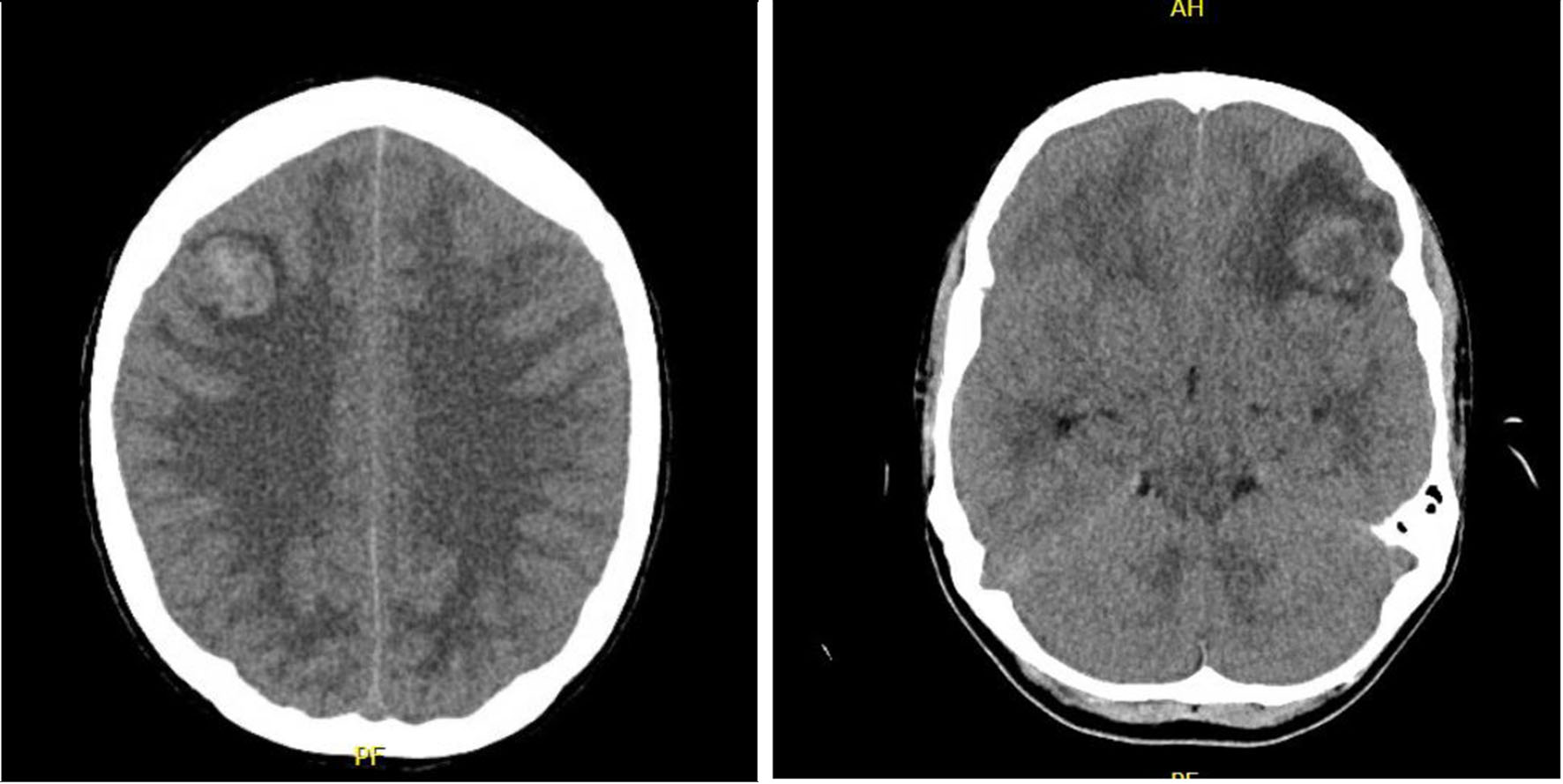
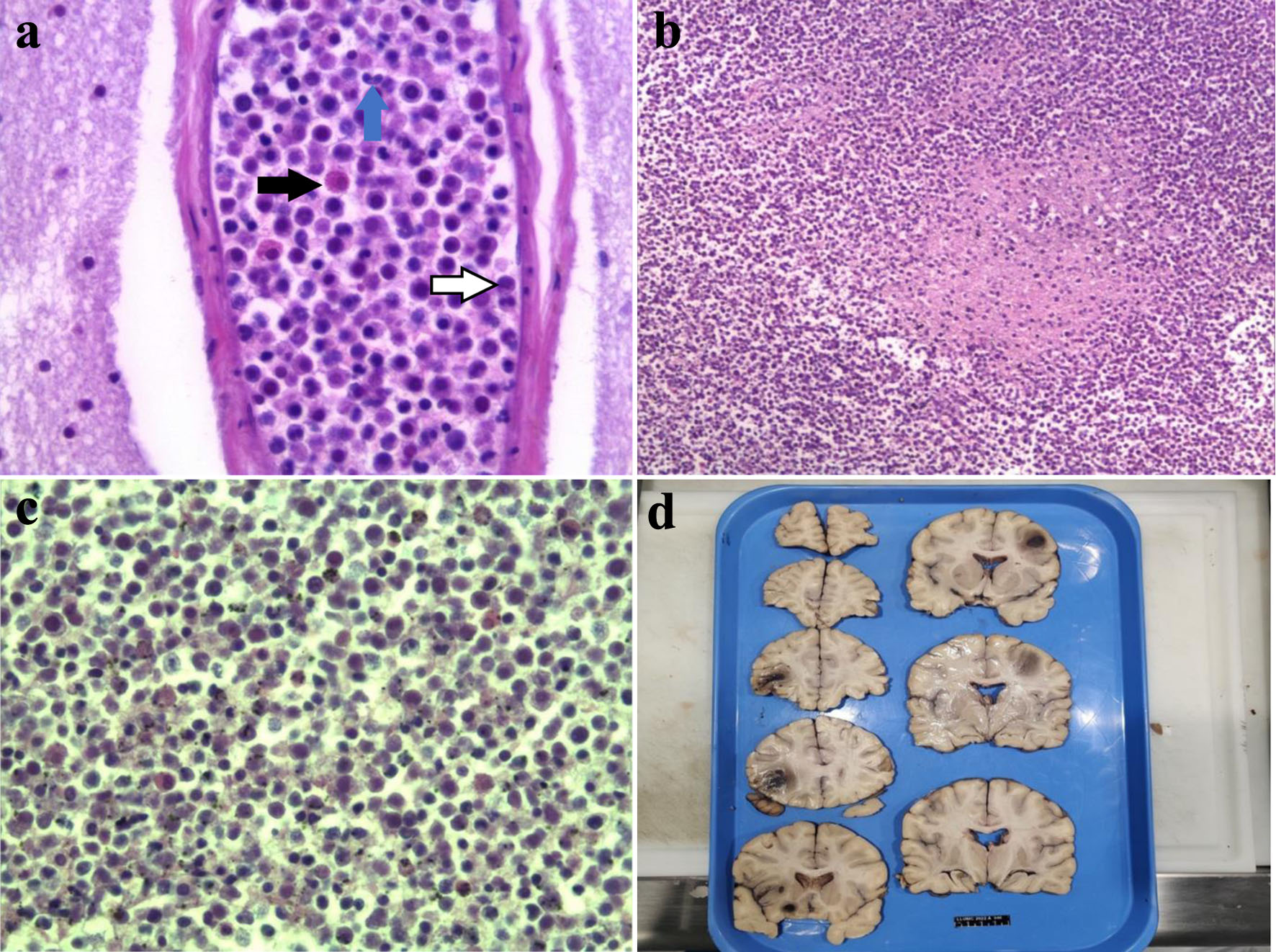
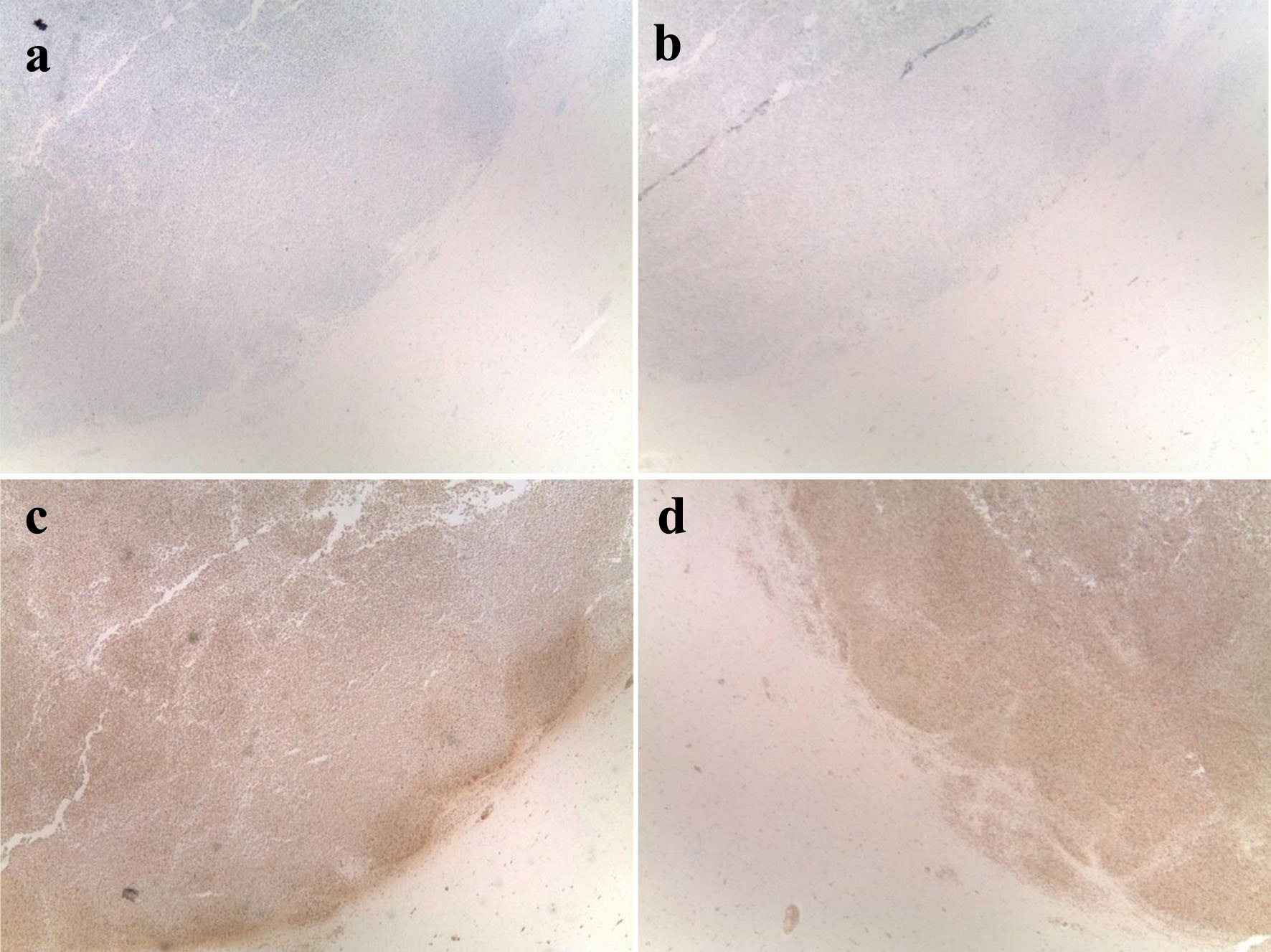
| Current case | 25/M | Known CML | CT of head showing multiple parenchymal leukemic infiltrates with mass effect; lesions with positive staining for MPO, CD43, and CD68 | Started on imatinib but changed to dasatinib due to concern for resistance; did not tolerate leukapheresis | Death |
| Jin et al [7] | 5/M | Newly diagnosed CML | Extramedullary blast crisis in CNS. BM aspirate revealed active hyperplasia of BM. + BCR/ABL1 | Methotrexate, dexamethasone, and cytarabine intrathecal injection therapy; HAD for three cycles, followed by second generation TKIs | CR |
| Radhika et al [8] | 15/F | CML on imatinib | MRI of brain showed thrombosis of posterior part of superior sagittal sinus. CSF showed large atypical looking cells comprising 48%, with hyperchromatic nuclei; CSF cytospin showed > 90% blasts | BMT not possible, as the patient did not have an HLA matched sibling donor. Imatinib dose increased and underwent six cycles of triple intrathecal chemotherapy and cranial radiotherapy | Lost to follow-up |
| Radhika et al [8] | 37/M | CML on imatinib | MRI of brain revealed bilateral multiple small infarcts with features of meningitis. CSF showed increased numbers of immature cells (30%); CSF cytospin showed 60% blasts. | BMT was not possible, as the patient did not have an HLA matched sibling donor. The dose of Imatinib was increased to 600 mg once daily, and six cycles of triple intrathecal chemotherapy and cranial radiotherapy were also given. | Death 3 months after CNS blast crisis due to CNS disease. |
| Abuelgasim et al [9] | 29/M | Newly diagnosed CML | CT of head showed new 4 cm left frontoparietal subdural collection, 1.5 cm left frontotemporal lobe collection, and right frontoparietal subdural collection. CSF showed 95% blasts. Flow cytometry of CSF showed blast cells + for CD34, CD33, CD11b, CD71 and CD13/CD117. BM showed chronic phase CML. | Whole brain radiation therapy and dasatinib therapy with AML induction with cytarabine and idarubicin + intrathecal methotrexate/cytarabine/hydrocortisone (allo-HSCT not recommended due to multiple infections/pancytopenia) | CR |
| Jain et al [10] | 35/M | Noncompliance in known CML | MRI of brain with heterogenous enhancement of falx cerebri and tentorium (pachymeningitis) and bilateral optic nerves. CSF flow cytometry showed myeloid blasts + CD13, CD33 (negative for CD10 and CD19). No mutation for TKI resistance. BM with 2% myeloblasts. | Imatinib and intrathecal methotrexate and dexamethasone | Death after two doses of intrathecal therapy |
| Healey et al [11] | 23/F | Newly diagnosed CML | MRI of brain after imatinib showed enhancement of left posterior frontal lobe including subarachnoid space. BM with 14% blasts (accelerated phase of CML), CSF with 51% blasts | Imatinib initially then started on dasatinib due to relapse. Underwent unmatched donor HSCT | CR |
| Chiba et al [12] | 30/M | Newly diagnosed CML | MRI of brain showed hypertrophic dura without obvious tumor. BM with increased myeloid cells (no specific number), CSF flow cytometry positive for CD10, CD19, HLADR, CD34 | Hydroxyurea, dasatinib, and hyperCVAD/MA therapy with dasatinib along with intrathecal methotrexate, cytarabine, and dexamethasone. Underwent allo-HSCT after whole brain radiation and total body radiation (with cyclophosphamide) | CR |
| Atilla et al [3] | 72/M | Progression of known chronic phase CML to blast crisis | MRI of brain showed enhancement of clivus and occipital condyles. BM with 42% blasts; CSF flow cytometry normal | Bosutinib with methotrexate, dexamethasone involvement. Radiotherapy and intrathecal methotrexate with cytarabine | CR |
| Gomez et al [13] | 33/M | Known CML, CNS involvement on imatinib | Normal head CT. Normal brain MRI. Unavailable CSF and serum flow cytometry | Intrathecal methotrexate, cytosine arabinoside, dexamethasone; then started on dasatinib. | CR but with persistent severe visual impairment |
| Neumann et al [14] | 25/F | CML with previous HSCT and relapses treated with DLIs and imatinib | Leptomeningeal relapse confirmed by CSF cytology and flow cytometry | Intrathecal methotrexate, cytarabine, and dexamethasone followed by high dose cytarabine for persistent neurological symptoms. DLI in increasing doses with addition of nilotinib | CR for 15 months followed by relapse and death |
| Park et al [15] | 54/M | Known CML | Diffusion MRI of brain with MRA revealed abnormal leptomeningeal enhancement of both paramedian gyri. CSF confirmed CNS involvement | Dasatinib, intrathecal methotrexate, and cranial irradiation therapy | CR |
| Kim et al [16] | 42/M | CML on imatinib | Craniotomy for increased intracranial pressure from mass of bilateral cerebellar hemispheres. Underwent partial resection with biopsy confirming isolated CNS lymphoid blast crisis | Cytarabine, methotrexate, and hydrocortisone with imatinib | Death 15 days after craniectomy |
| Beyazit et al [17] | 46/F | CML treated with hydroxyurea and interferon-alpha/cytarabine followed by imatinib at remission | Lumbar MRI suggested malignant infiltration of the spinal cord. LP showed blastic cellular infiltration | Intrathecal methotrexate and craniospinal radiotherapy | Death from pulmonary aspergillosis |
| Gaur et al [18] | 30/M | CML on ponatinib | MRI of brain showed diffuse supratentorial and infratentorial leptomeningeal enhancement. CSF showed myeloblasts | Intrathecal cytarabine and craniospinal irradiation | CR; pending allogeneic SCT |
| Rajappa et al [19] | 39/M | CML on Imatinib | MRI of brain showed meningeal enhancement and CSF positive for blasts | Cranial radiotherapy and triple intrathecal chemotherapy | CR |
| Bornhauser et al [20] | 56/F | CML on imatinib | MRI of brain revealed minimal dural enhancement. LP revealed lymphoid blast crisis in CSF | Intrathecal cytosine arabinoside, methotrexate, and dexamethasone and irradiation of the total neuraxis | Death 22 days after HSCT |
| Bujassoum et al [21] | 42/F | Known CML | MRI of brain showed increased signal intensity in the periventricular area with LP showing CML blast crisis. Flow cytometry showed an increase in myeloid blasts CD34+, CD117+. BM showed BCR/ABL1 fusion | Intrathecal methotrexate and cytarabine | CR |
| Johnson et al [22] | 50/M | Known CML | CSF showed CD19+, CD10+, CD34+ | Intrathecal chemotherapy and HSCT | Death |
| Matsuda et al [23] | 17/M | CML on imatinib | CT of head demonstrated no specific signs of meningeal and cerebral involvement. LP revealed blasts in the CSF | Intrathecal chemotherapy with cytosine arabinoside, methotrexate, and dexamethasone and whole-brain radiation | CR |
| Aichberger et al [24] | 52/M | CML on imatinib | CT of head and MRI of brain normal. LP showed myeloblasts. CD34+, HLADR+, CD117+ | Intrathecal liposomal cytarabine and intracranial radiation | CR |
| Aichberger et al [24] | 73/F | CML on imatinib | CT of head showed leukoencephalopathy and microangiopathy without meningeal involvement. CD117+, CD13+, CD33+, CD34+ | Intrathecal liposomal cytarabine | CR |
| Barlow et al [25] | 68/M | CML on imatinib | CSF showed increased white blood cell count | Intrathecal methotrexate and dexamethasone; switched to dasatinib. Underwent cranial irradiation | Clinical improvement |
| Altintas et al [26] | 39/M | CML on hydroxyurea and imatinib | MRI of brain showed meningeal enhancement at the frontoparietal region and tentorium. CSF showed lymphoblasts. | Radiation, intrathecal chemotherapy, and imatinib | CR |
| Lee et al [27] | 39/M | CML on imatinib | MRI of brain with abnormal high signal intensity in the petrous region bilaterally | Intrathecal cytarabine and methotrexate and increased imatinib dose | CR |
| Isobe et al [28] | 61/M | Known CML | CT of head showed swelling of cerebellar cortex and fourth ventricle dilatation. CSF showed lymphoblasts and flow cytometry showed blasts positive for CD10, CD19, and CD20. | Intrathecal methotrexate and dexamethasone, and allogeneic HSCT with thiotepa, etoposide and cyclophosphamide; also underwent optic nerve irradiation | CR |
| Thomas et al [29] | 33/M | CML treated with hydroxyurea, cytosine arabinoside, dasatinib, and SCT | MRI of brain and spine unremarkable. CSF showed blast-like cells positive for MPO and BCR-ABL fusion signal in 91% of cells and flow cytometry showed myeloid associated antigens. | Intrathecal methotrexate and craniospinal irradiation. Started on nilotinib. | CR |
| Fuchs et al [30] | 64/F | CML treated with imatinib followed by cytosine arabinoside and mitoxantrone and hydroxyurea | MRI of brain revealed leukemic infiltration of lateral ventricles walls and hydrocephalus. CSF with about 50% immature blasts with highly elevated BCR-ABL/ABL ratio | Intrathecal cytarabine, methotrexate, and dexamethasone followed by dasatinib | CR |
| Nishimoto et al [31] | 22/M | CML on imatinib | CML blast crisis in CNS after 29 months of therapy | Allogeneic HSCT following combination therapy with dasatinib, intrathecal chemotherapy and cranial irradiation. Followed by dasatinib maintenance therapy | CR |