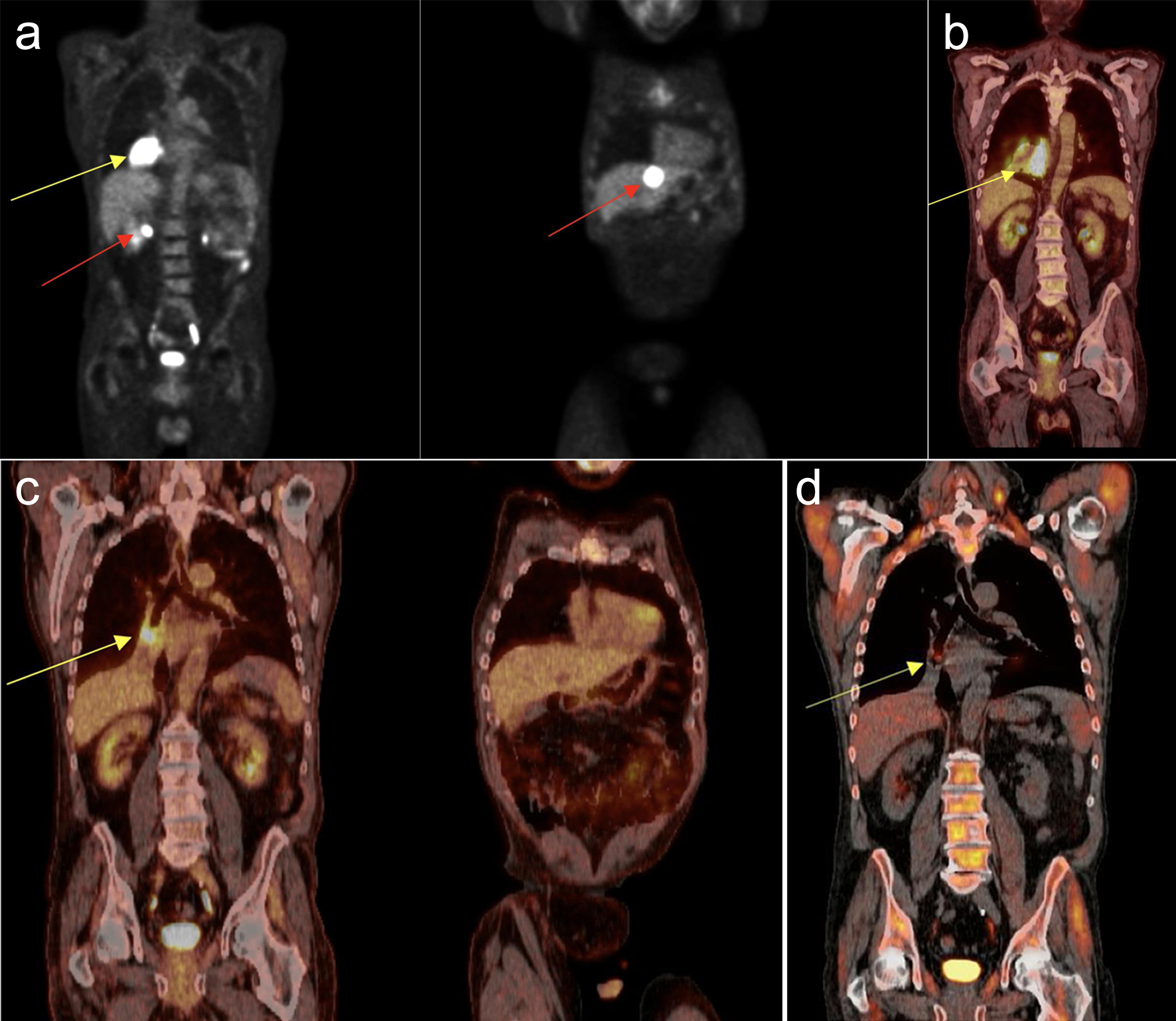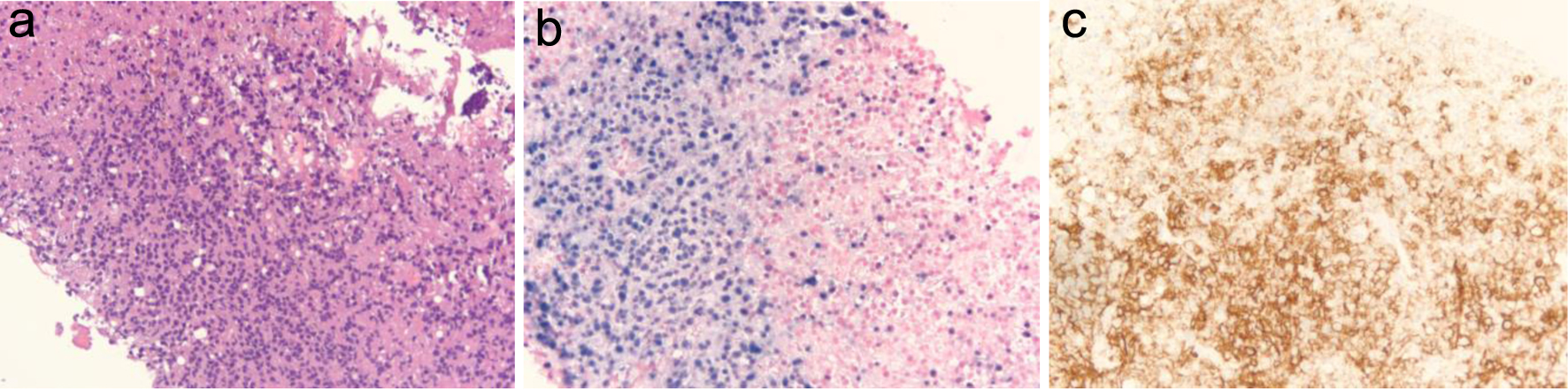
Figure 1. (a) Liver core biopsy showing monomorphic proliferation of neoplastic cells (at × 20 magnification). (b) Ebstein-Barr virus (EBV) stain showing positive nuclear staining of EBV-infected cells (at × 20 magnification). (c) CD20 stain showing positive membranous staining of B cells (at × 20 magnification).