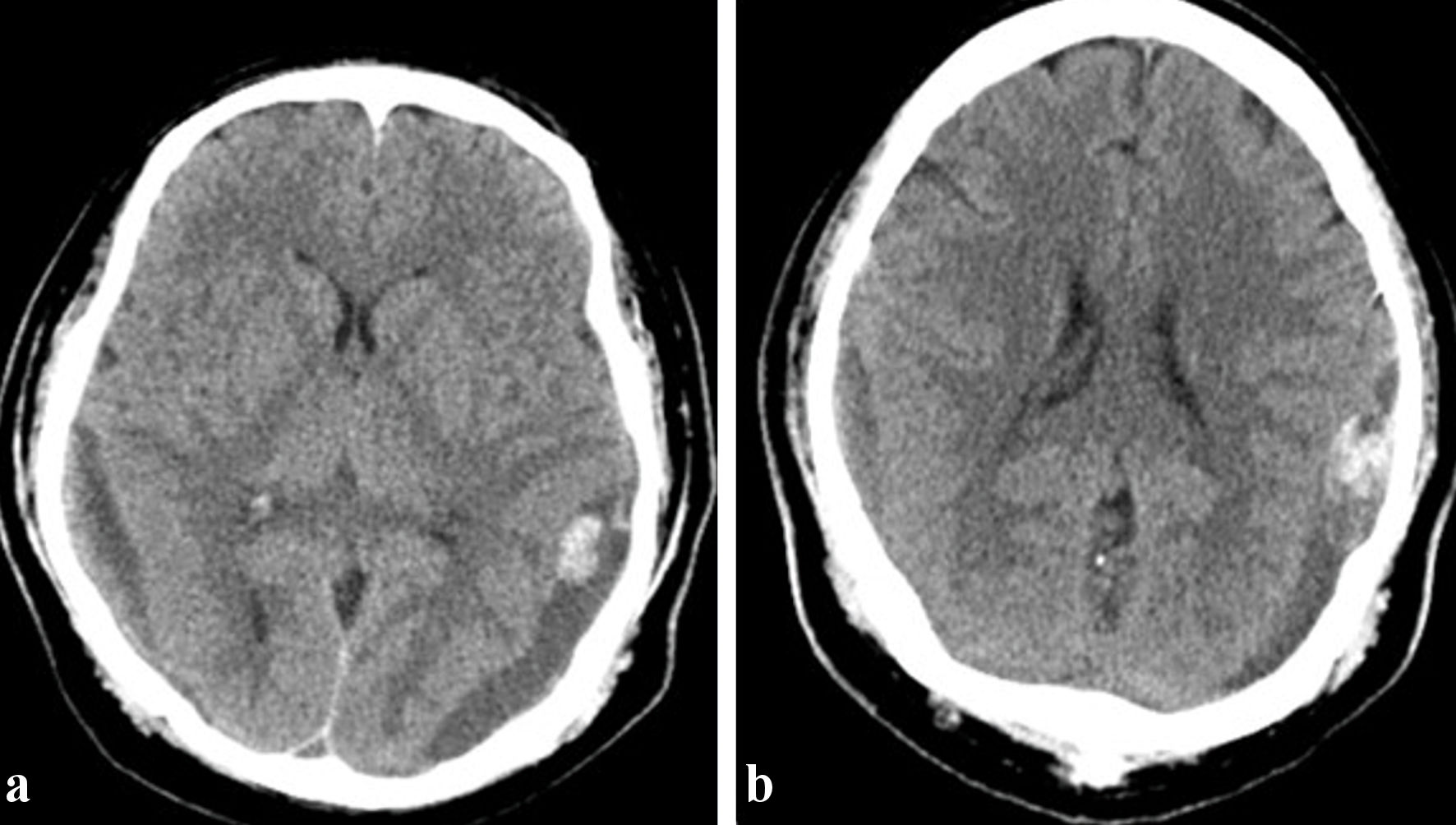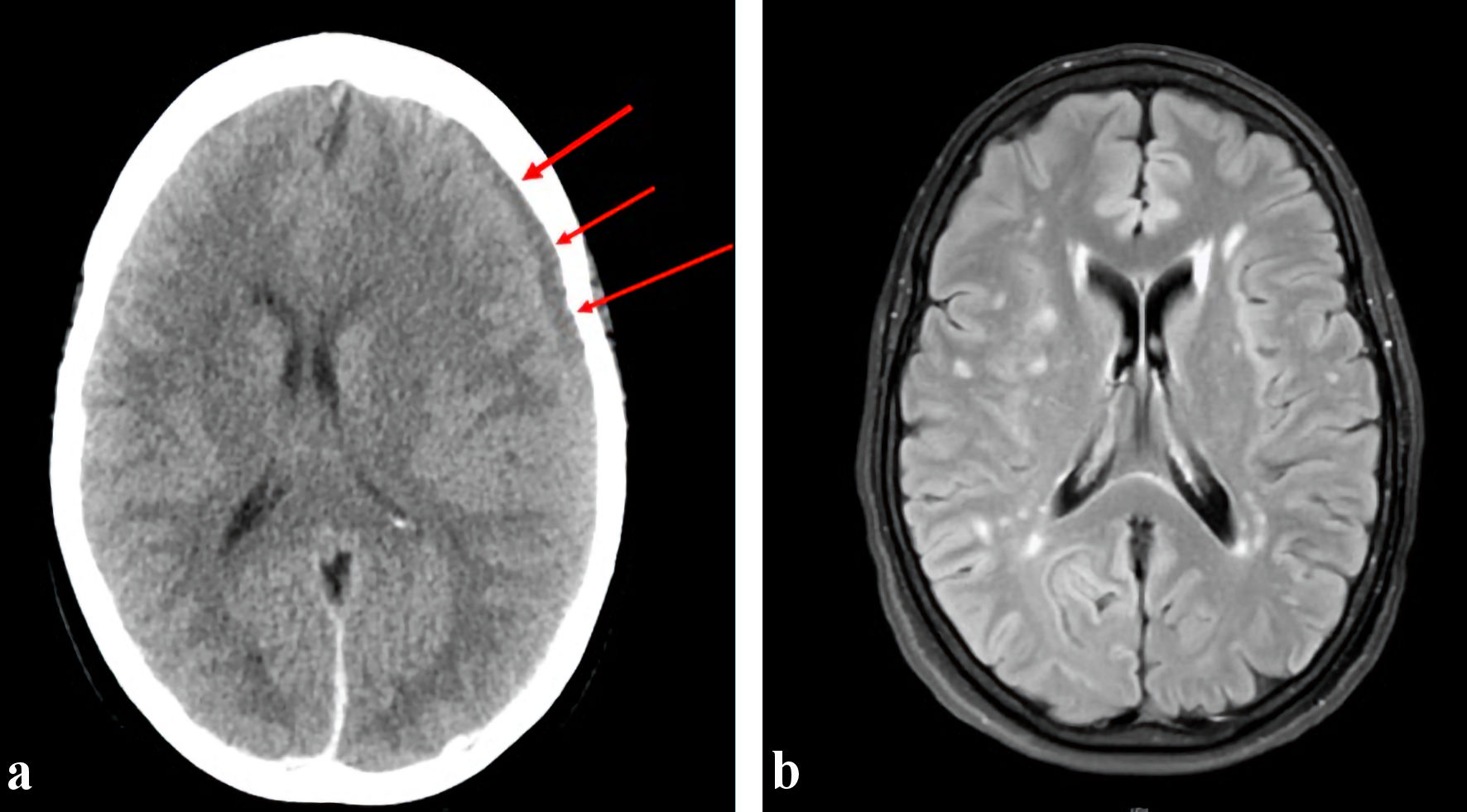
Figure 1. (a) Preoperative CT head showing left cerebral convexity subdural hematoma (arrows), measuring up to 1.1 cm in thickness. There is an associated rightward midline shift of 6 mm at the level of the foramen of Monro and trace subarachnoid hemorrhage in the left frontal lobe. (b) MRI brain done 7 months later showing resolved subarachnoid hemorrhage along the left cerebral convexity and right parafalcine region with no evidence of residual or recurrence hemorrhage. CT: computed tomography; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging.