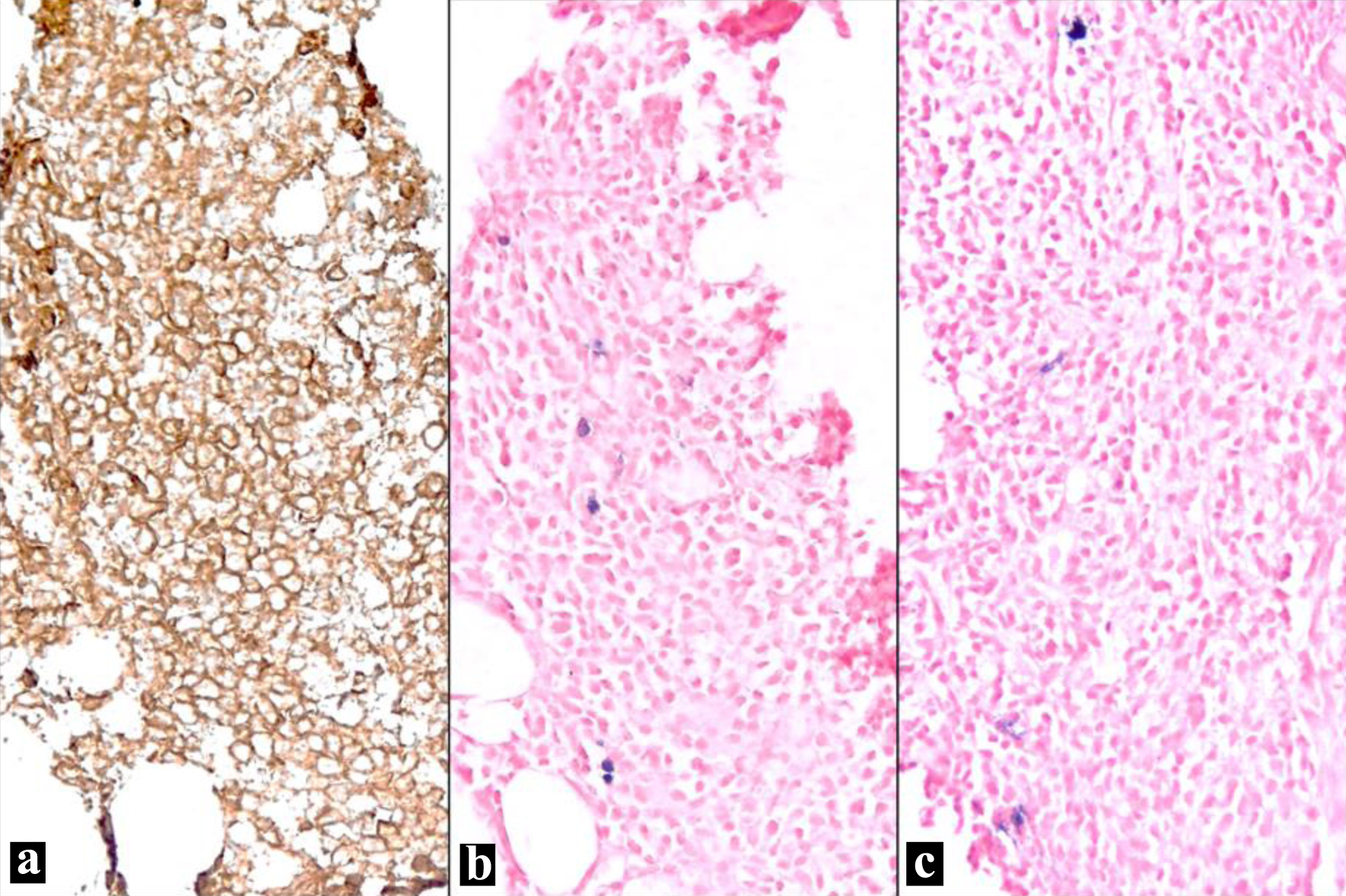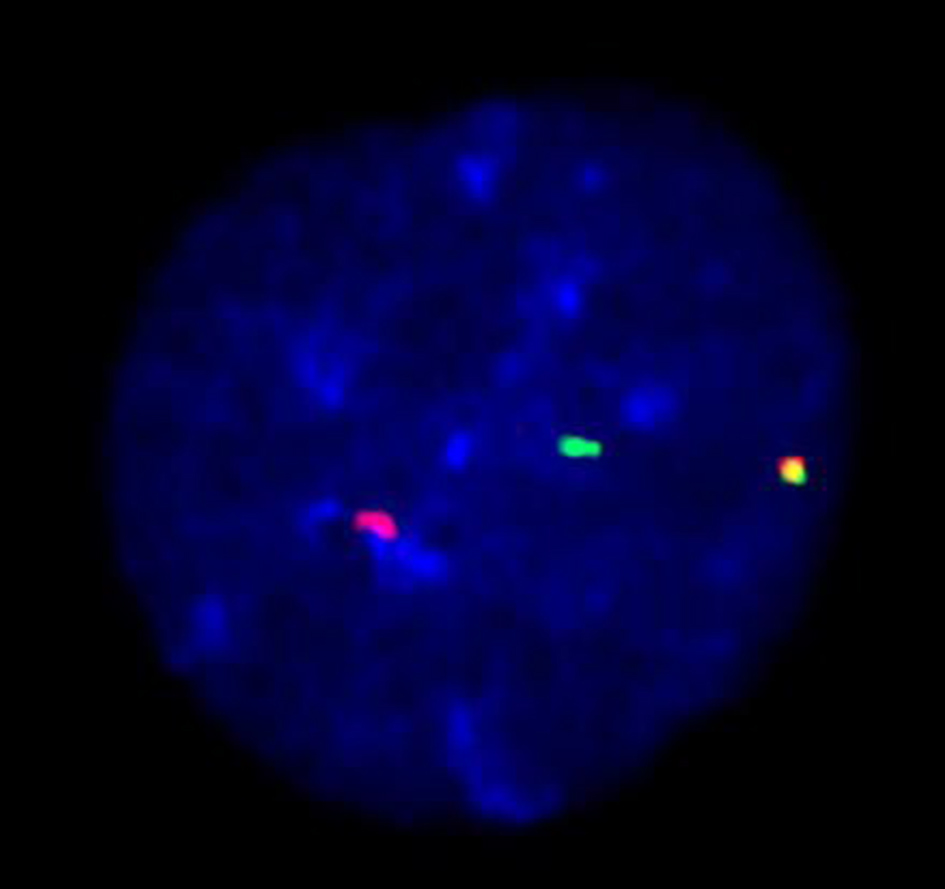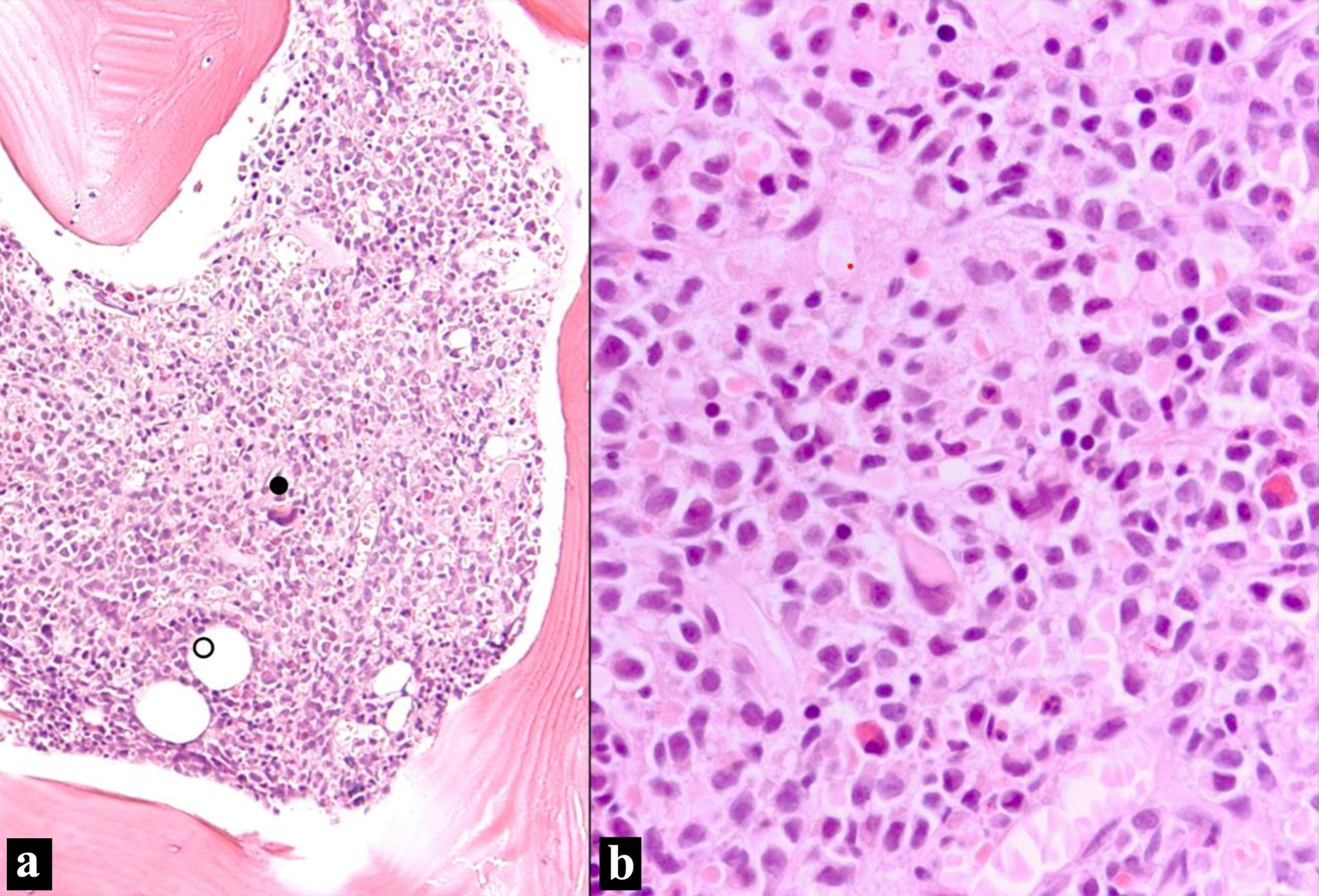
Figure 1. Bone marrow biopsy (H&E stain). (a) Bone marrow intertrabecular space diffusely infiltrated by sheets of non-cohesive cells. Residual bone marrow elements are scattered (• megakaryocyte; ○ adipocytes) (H&E, × 100 optical magnification). (b) Sheet of atypical plasma cells infiltrating with residual bone marrow elements. The plasma cells have eccentric nuclei with mild atypia and moderate eosinophilic cytoplasm with perinuclear hofs (H&E, × 400). H&E: hematoxylin and eosin.