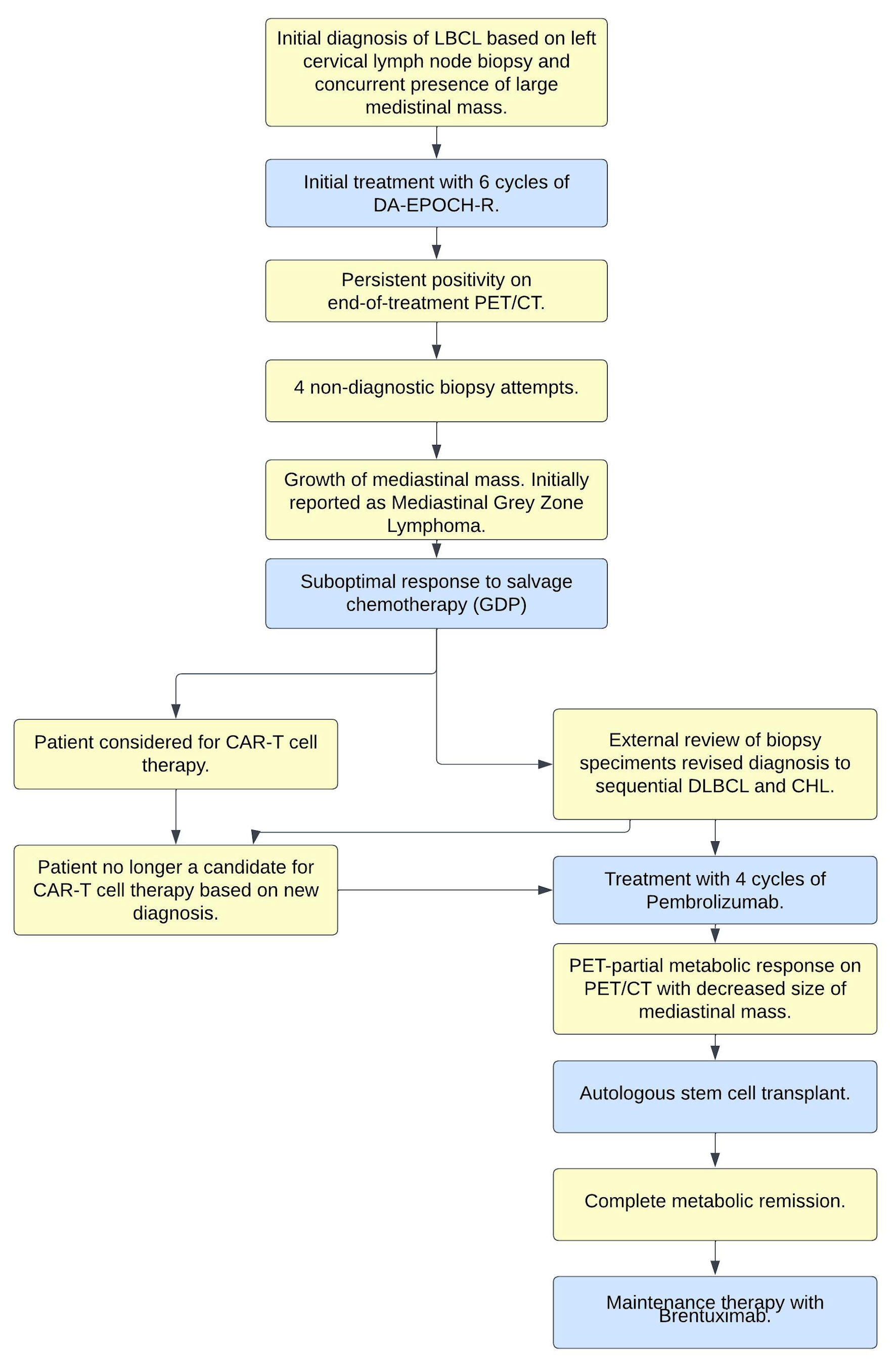
Figure 1. Clinical-pathologic summary of events. LBCL: large B-cell lymphoma; CHL: classical Hodgkin lymphoma; DA-EPOCH-R: dose-adjusted EPOCH-R; DLBCL: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; PET/CT: positron emission tomography/computed tomography; EPOCH-R: etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab; GDP: gemcitabine, dexamethasone, cisplatin; CAR: chimeric antigen receptor.
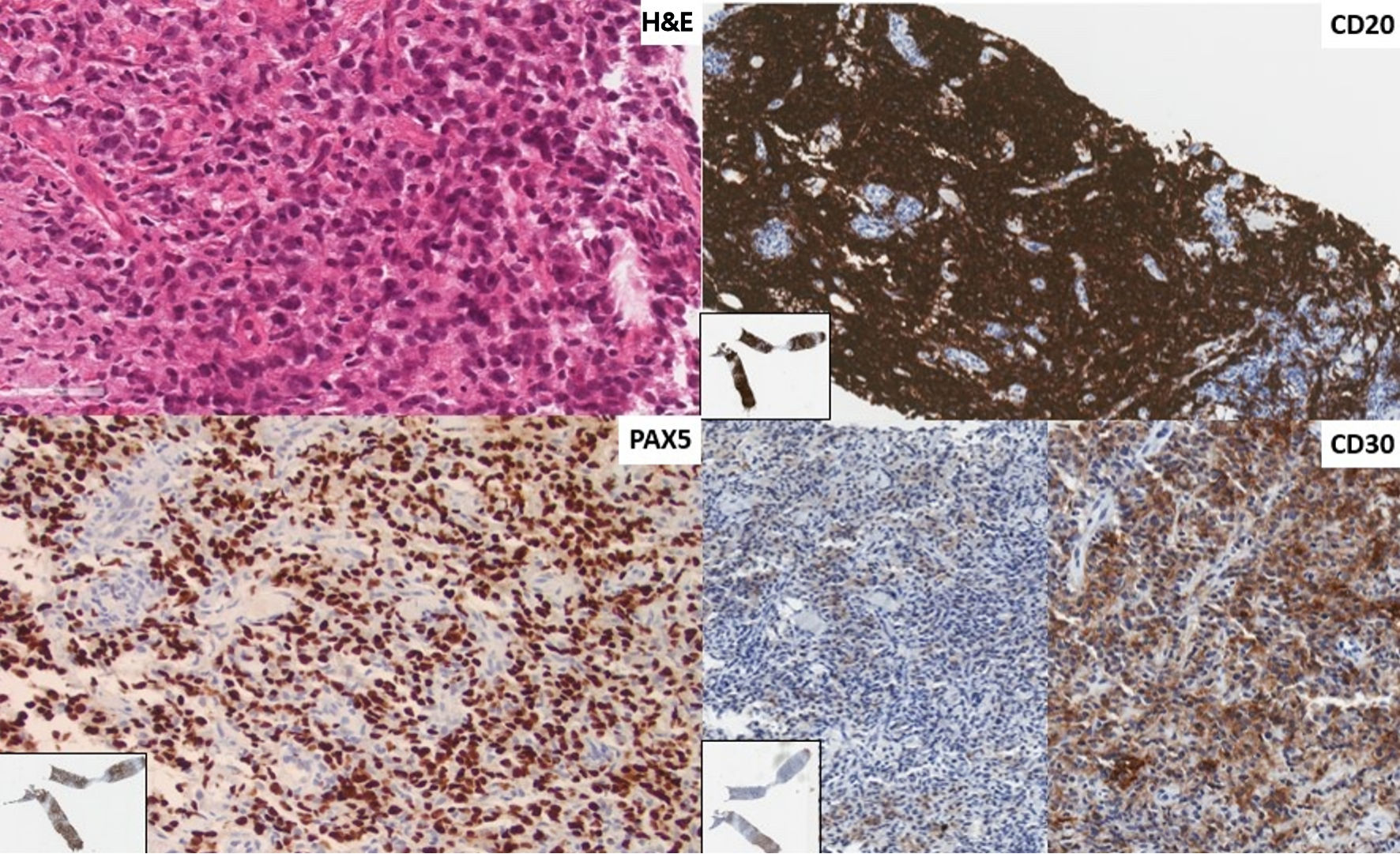
Figure 2. First instance of lymphoma shown in a biopsy of a left neck lymph node. The revised diagnosis is of a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of germinal center phenotype (CD10-, BCL6+, MUM1-). The architecture of the lymph node parenchyma is effaced by sheets of large rounded lymphoid cells (H&E stain × 400). There is diffuse immunoreactivity for CD20 and PAX5, and patchy staining for CD30 (× 200, insert: low power). There was no positivity for CD15 or CD23. Tumor cells are PDL1+. H&E: hematoxylin and eosin; PDL1: programmed death ligand-1; BCL6: B-cell lymphoma 6; MUM1: multiple myeloma 1; PAX5: paired box 5.
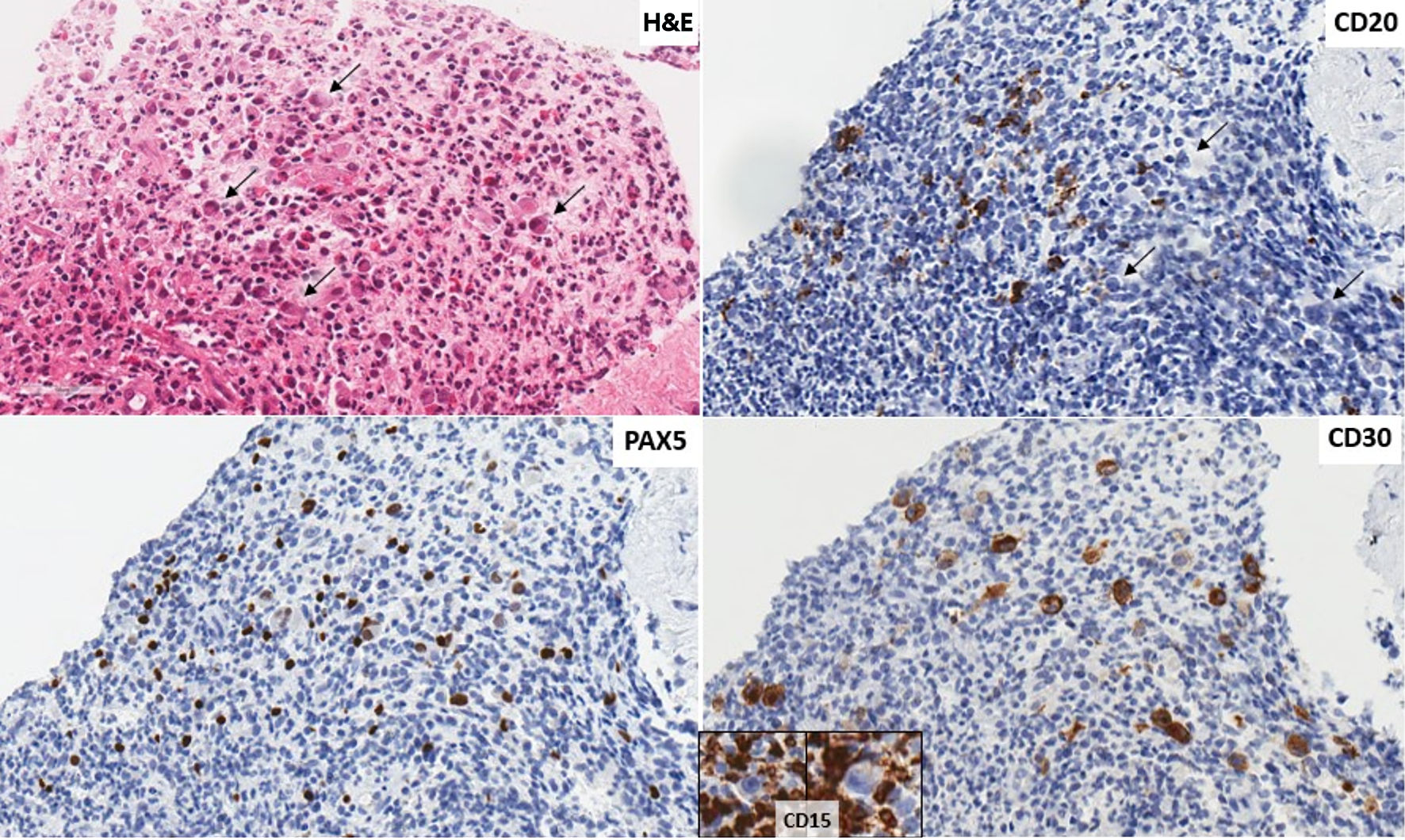
Figure 3. Second instance of lymphoma shown in a biopsy of a mediastinal mass. The revised diagnosis is of a classic Hodgkin lymphoma. There are scattered large cells with Reed Sternberg and Hodgkin morphology (arrows) scattered in an eosinophil rich mixed lymphoid background (H&E stain, × 400). Tumor cells (arrows) that do not show immunoreactivity for CD20 (× 400), are positive for PAX5 (× 400), CD30 (× 400) and negative for CD15 (insert, background inflammatory cells positive). Tumor cells are PDL1+. H&E: hematoxylin and eosin; PDL1: programmed death ligand-1; PAX5: paired box 5.


