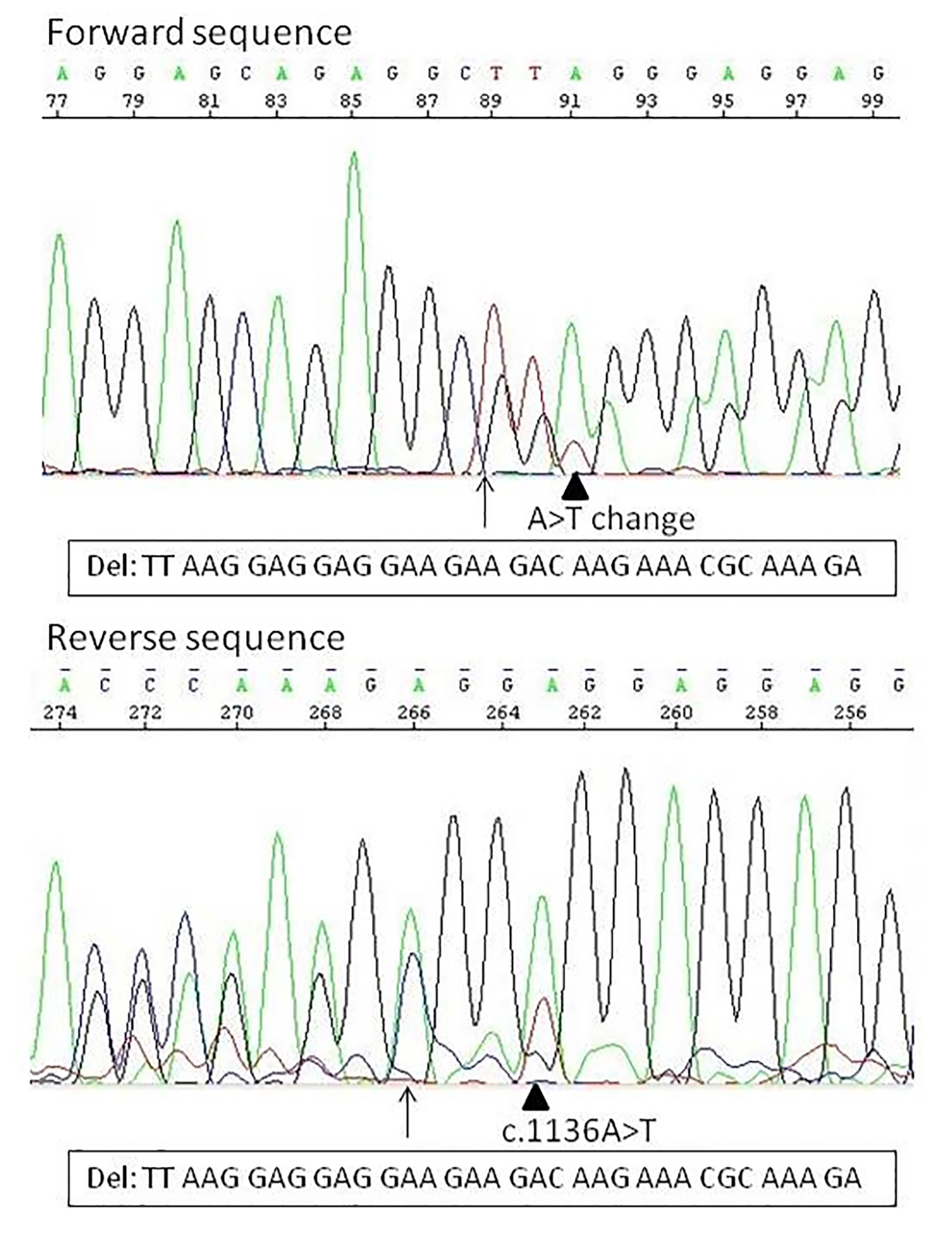
Figure 1. The two types of calreticulin mutation identified in this study. Arrow indicates the position of the deletion. The arrowhead indicates the A>T nucleic acid change, in forward sequence at position c.1102, and in reverse sequence at the original c.1136 position. In forward direction already the nucleic acid change can be seen: by the arrow the normal sequence is TTAAG, the deleted sequence should be GGAGG, what means that at position 91 (at the arrowhead, c.1102) should be only an A, instead of an A/T. The reverse direction confirms that the nucleic acid change is on the deleted allele.
