| Response, n (%); (Clopper-Pearson 95% CI) | 24 (63.2); (46.0; 78.2) |
| Time to Response (days), median (range) | 1 (1 - 6) |
| Duration of Response (days), estimate (Kaplan Meier 95% CI) | 13.5 (10.0; 20.0) |
| Loss of Response, n (%); (Clopper-Pearson 95% CI) | 17 (70.8); (48.9; 87.4) |
| No Response, n (%); (Clopper-Pearson 95% CI) | 14 (36.8); (21.8; 54.0) |
| Complete Response, n (%); (Clopper-Pearson 95% CI) | 11 (28.9); (15.4; 45.9) |
| Time to Complete Response (days), median (range) | 2 (1 - 8) |
| Duration of Complete Response (days), estimate (Kaplan Meier 95% CI) | 12 (10.0; 18.0) |
| Loss of Complete Response, n (%); (Clopper-Pearson 95% CI) | 9 (81.8); (48.2; 97.7) |
| No Complete Response, n (%); (Clopper-Pearson 95% CI) | 27 (71.1); (54.1; 84.6) |
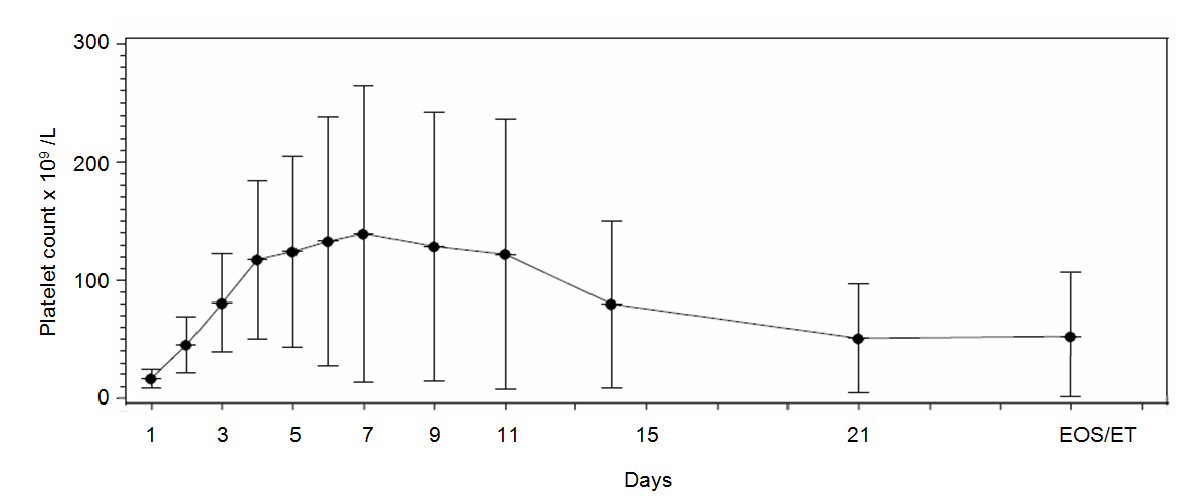
| Maximum platelet count (× 109)*, mean (Hodges-Lehmann 95% CI) | 165 (113; 189) |
| Time to maximum platelet count (days)†, median (Kaplan Meier 95% CI) | 4.0 (3.0; 6.0) |