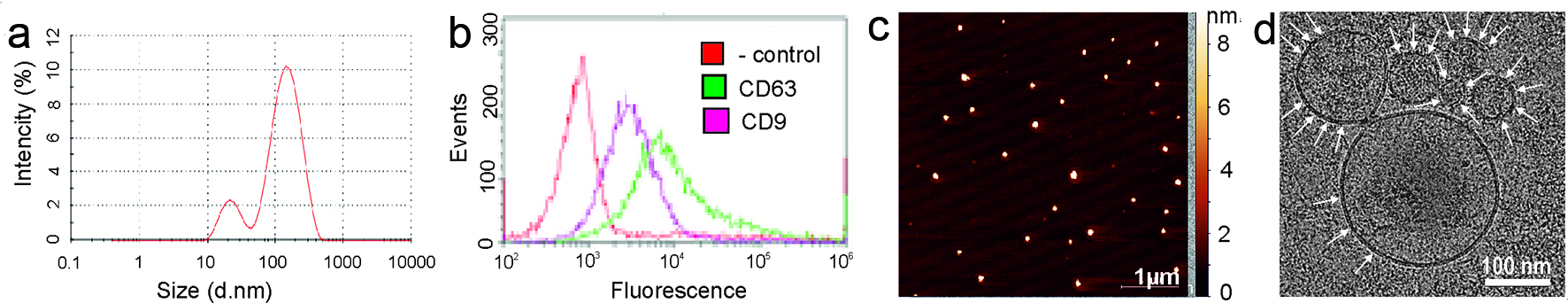
Figure 1. Exosomes characteristics. (a) Exosome size was estimated by dynamic light scattering (DLS). (b) Flow cytometry analysis of exosomes for the surface expression of exosomal markers CD9 and CD63 was carried out by ready to use kit for FACS analysis of purified exosomes (HansaBioMed). Negative control Exo(-) was performed without any vesicles. (c) The surface topography of plasma exosomes obtained with atomic force microscopy (AFM). The scale bar is 1 µm. On the right is the pseudocolor ruler indicating the particles’ height (nm). (d) Cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) of the exosomes derived from plasma. The scale bar is 100 nm.
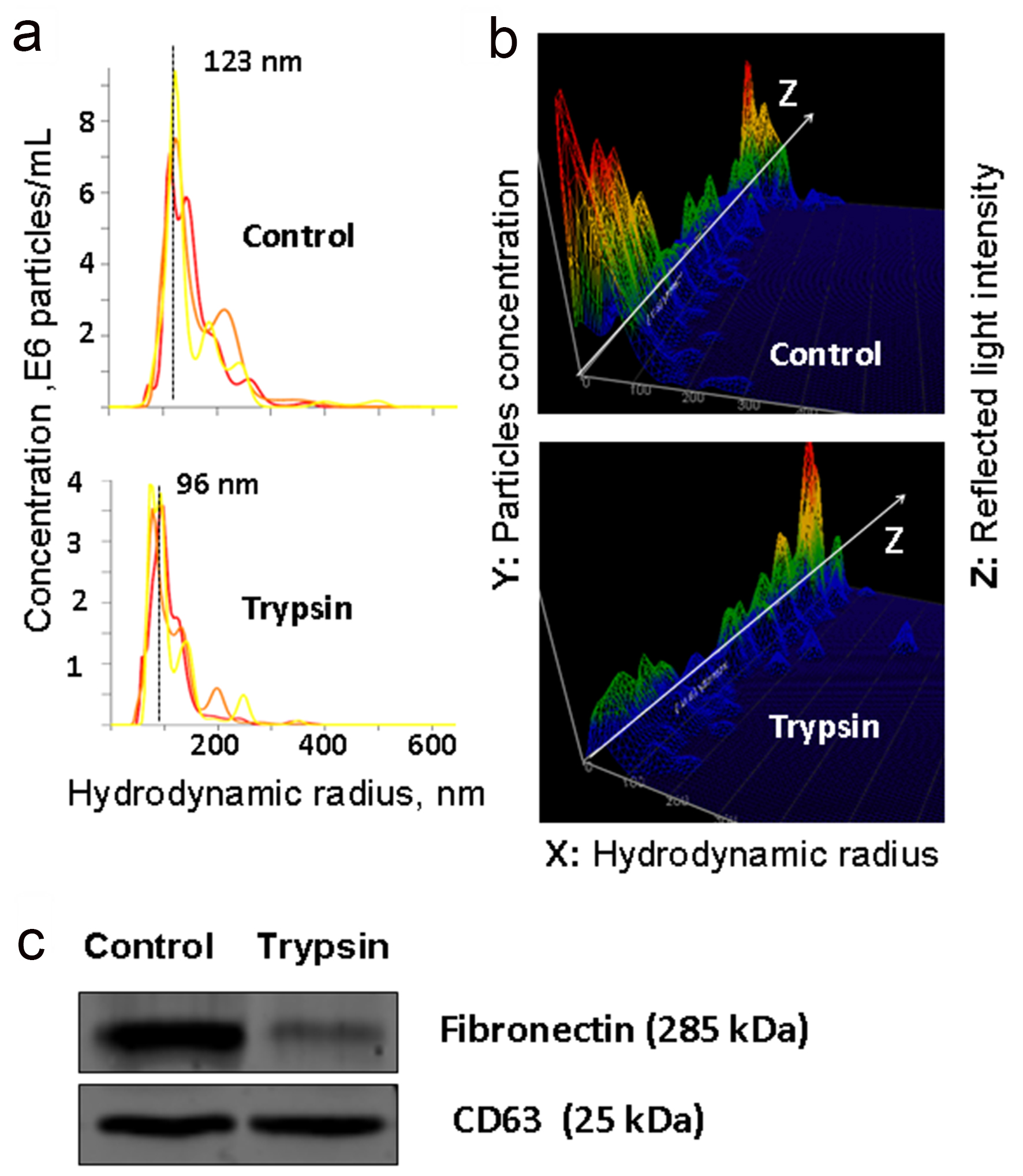
Figure 2. Analysis of trypsinized and intact plasma exosomes. (a and b) The results of nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) of exosomes isolated from plasma and treated with trypsin: the ratio of the size and concentration of exosomes (a); a three-dimensional graph, the Z axis shows changes in characteristics of light reflected from the surface of exosomes (b). (c) WB detection of fibronectin (FN) and exosomal marker CD63 in exosomes isolated from native plasma and exosomes treated with trypsin.
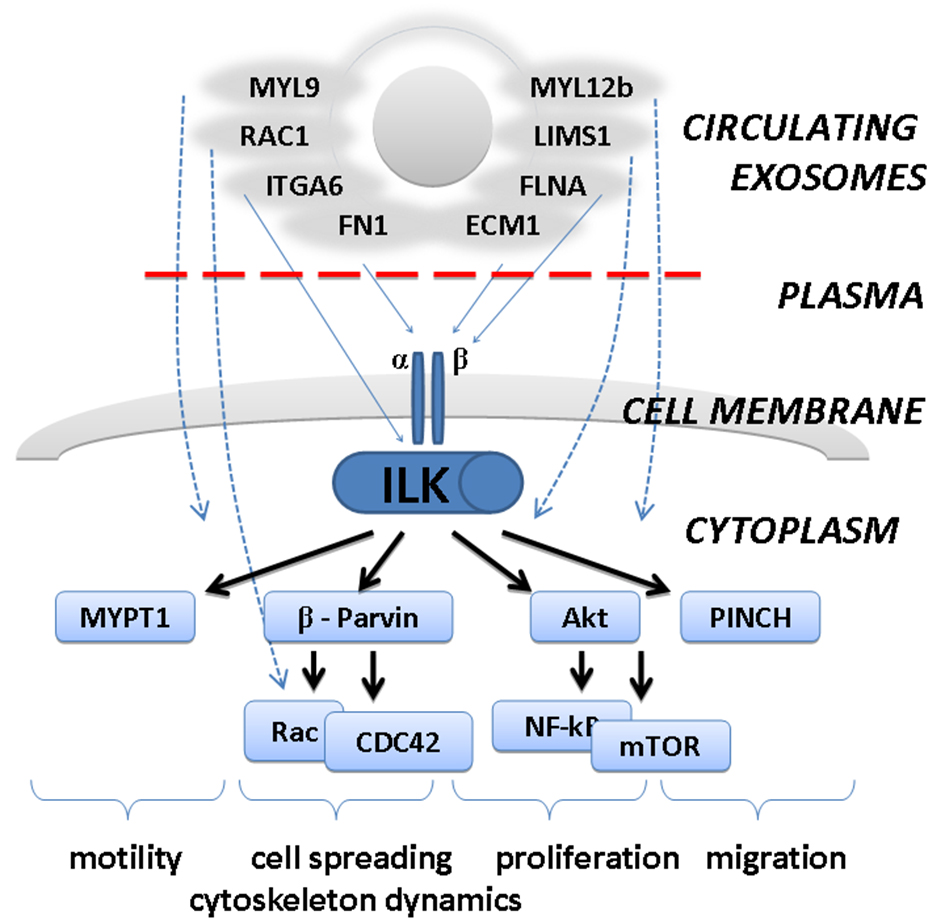
Figure 3. Predicted involvement of exosome-attached extracellular proteins in integrin-linked kinase (ILK) pathway. Plasma proteins attached to the surface of circulating exosomes may affect biology of the cells by interaction with surface receptors (integrins) and activation of downstream ILK-pathway. This would lead to stimulation of cellular migration, motility, proliferation, etc.


