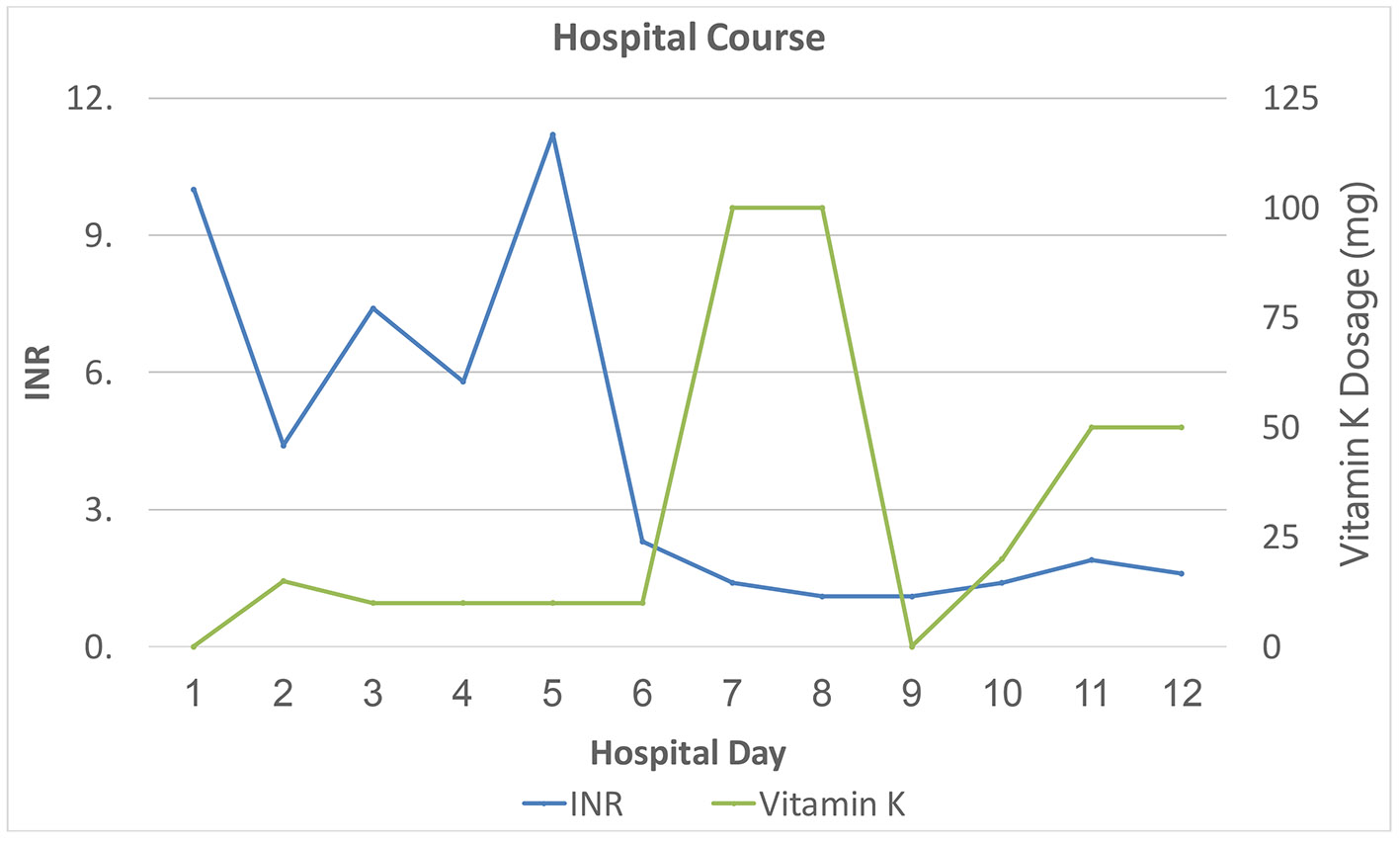
Figure 1. Inpatient course: INR in relation to treatment (plasma infusion: three units on the first day of hospitalization and one more unit on day 3). INR: international normalized ratio.
| Journal of Hematology, ISSN 1927-1212 print, 1927-1220 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Hematol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.thejh.org |
Case Report
Volume 8, Number 4, December 2019, pages 155-159
Superwarfarin Exposure: An Important Uncommon Cause of Painless Bleeding
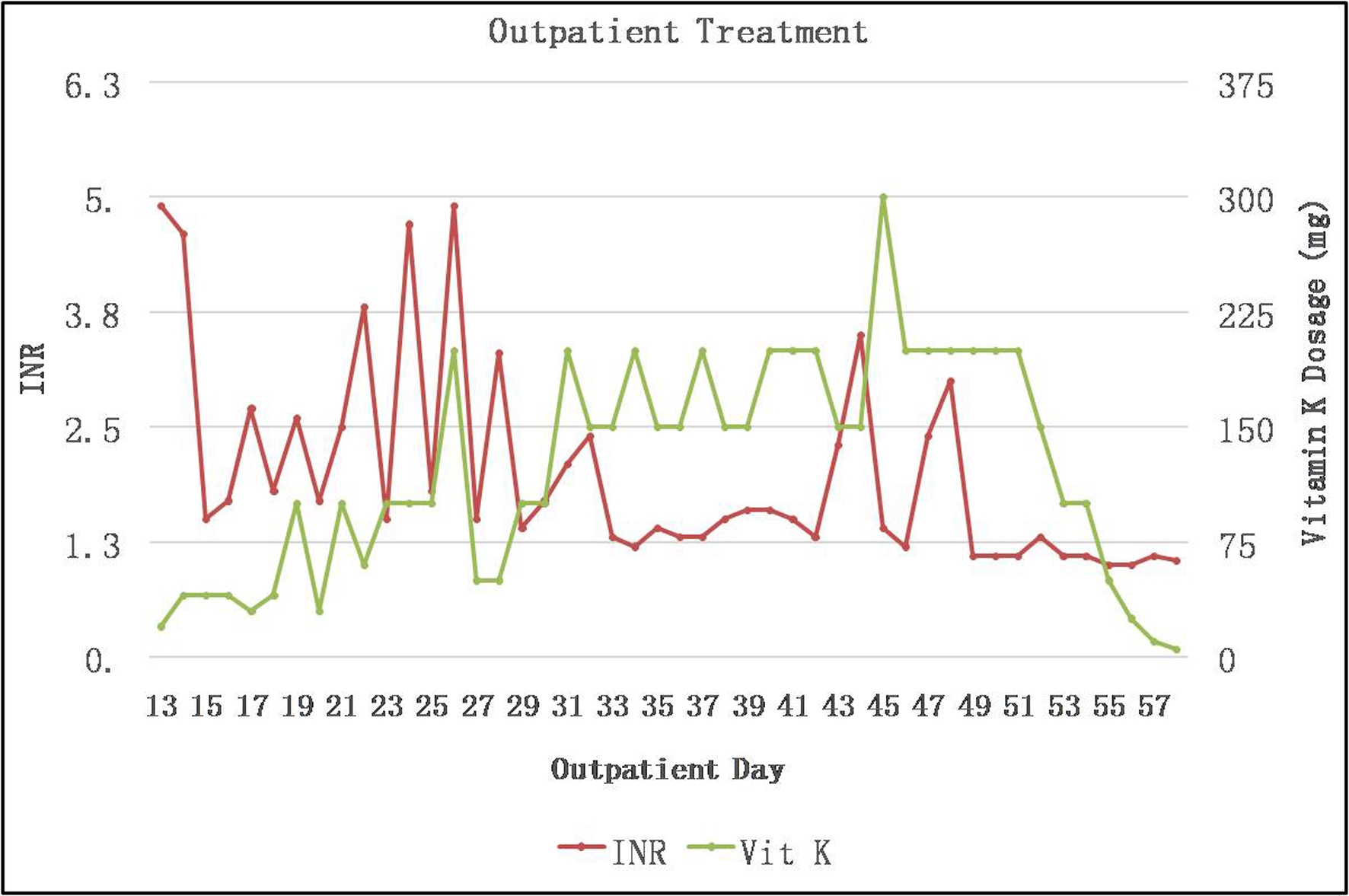
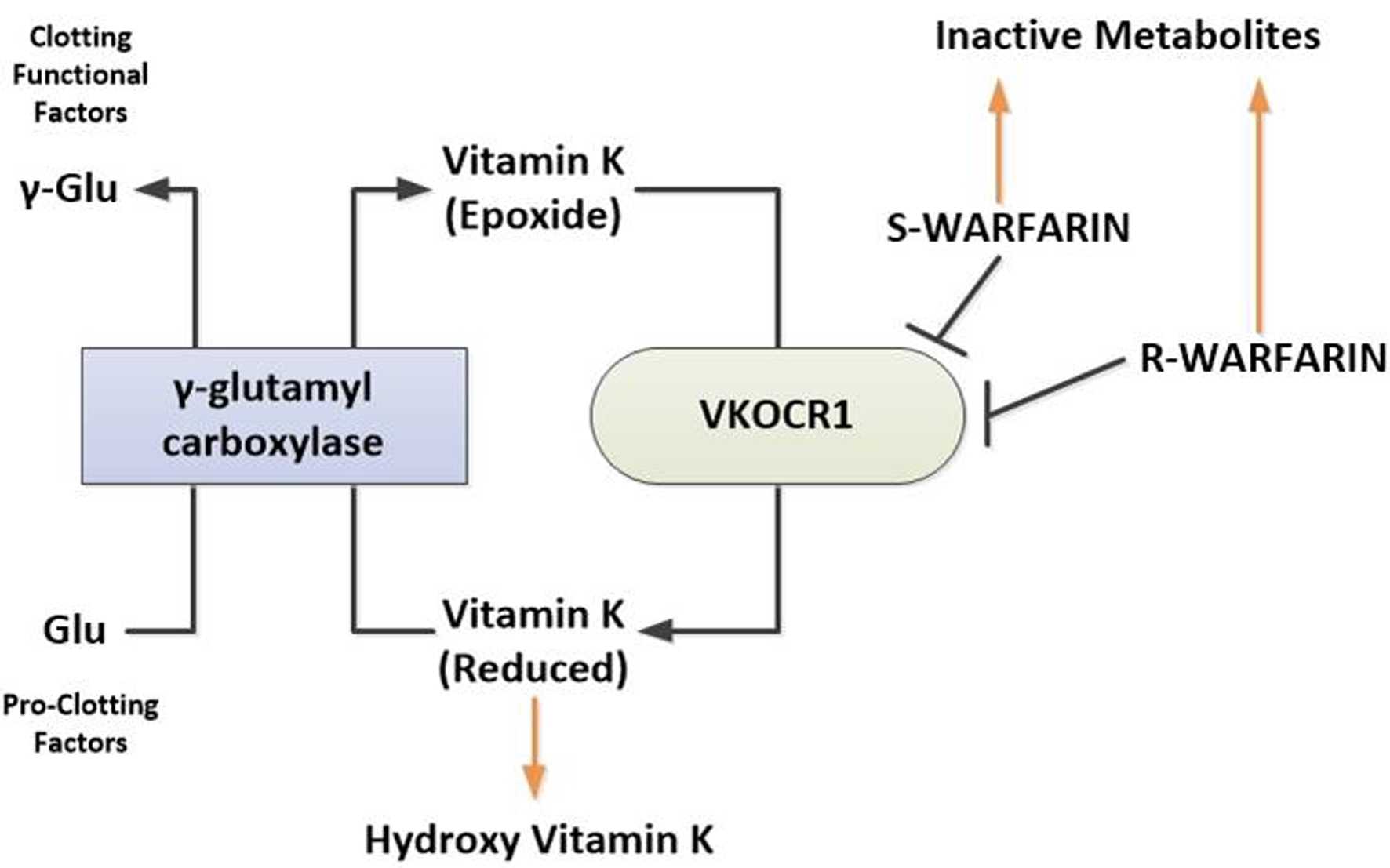
Figures

Table
| Analyte | Result (reference interval) |
|---|---|
| aVitamin K dependent factors. PT: prothrombin time; aPTT: activated partial thromboplastin time; VWF: von Willebrand factor; APL: acute promyelocytic leukemia. | |
| Initial screening tests | |
| Prolonged PT evaluation | 24.2 s (9 - 11.5) |
| PT immediate mix | 11.7 s (9 - 11.5) |
| Prolonged aPTT evaluation | 40 s (22 - 34) |
| aPTT immediate mix | 28 s (22 - 34) |
| Follow-up studies | |
| Procoagulant factors | |
| Factor II activitya | 37% (70-150%) |
| Factor V activity | 110% (65-150%) |
| Factor VII activitya | < 1% (60-175%) |
| Factor VIII activity | 152% (60-180%) |
| Factor IX activitya | 15% (50-160%) |
| Factor IX antigena | 1.11 (0.64 - 1.29) |
| Factor X activitya | 27% (70-150%) |
| Factor XI activity | 94% (65-150%) |
| Factor XII activity | 92% (50-150%) |
| Von Willebrand factor antigen | 146% (50-217%) |
| Ristocetin cofactor activity | 82% (42-200%) |
| VWF multimeric study | Normal |
| Prothrombotic risk factors | |
| ATIII antigen | 130% (70-150%) |
| ATIII activity | 125% (80-120%) |
| Protein C antigena | 74% (70-140%) |
| Protein C activitya | 58% (70-180%) |
| Total protein S antigena | 91% (70-140%) |
| Free protein S antigena | 57% (57-171%) |
| APL studies (including lupus anticoagulant, cardiolipin and beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies) | Negative (negative) |
| Serum immunofixation studies | Negative (negative) |
| Brodifacoum (qualitative test) | Positive (negative) |