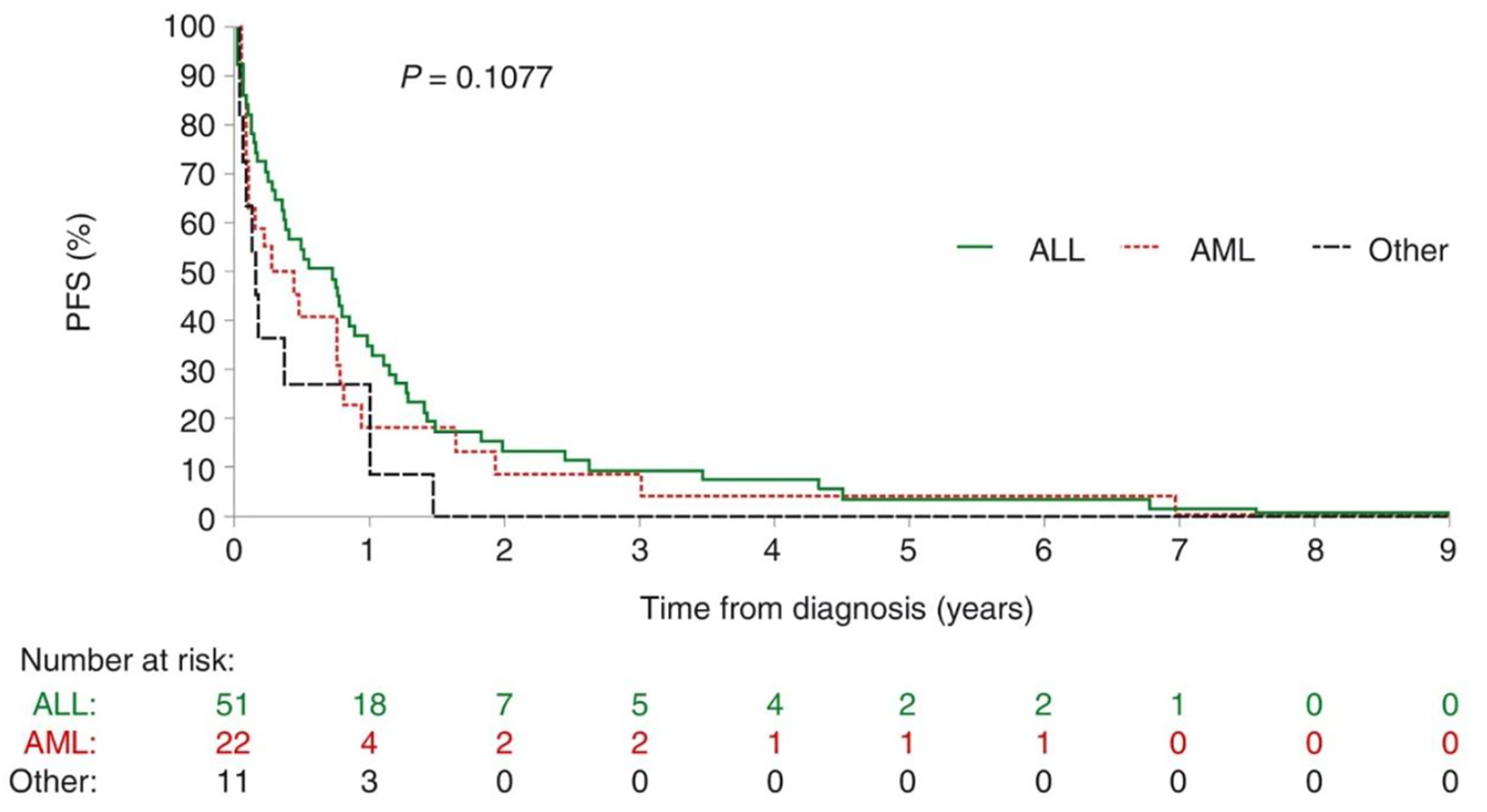
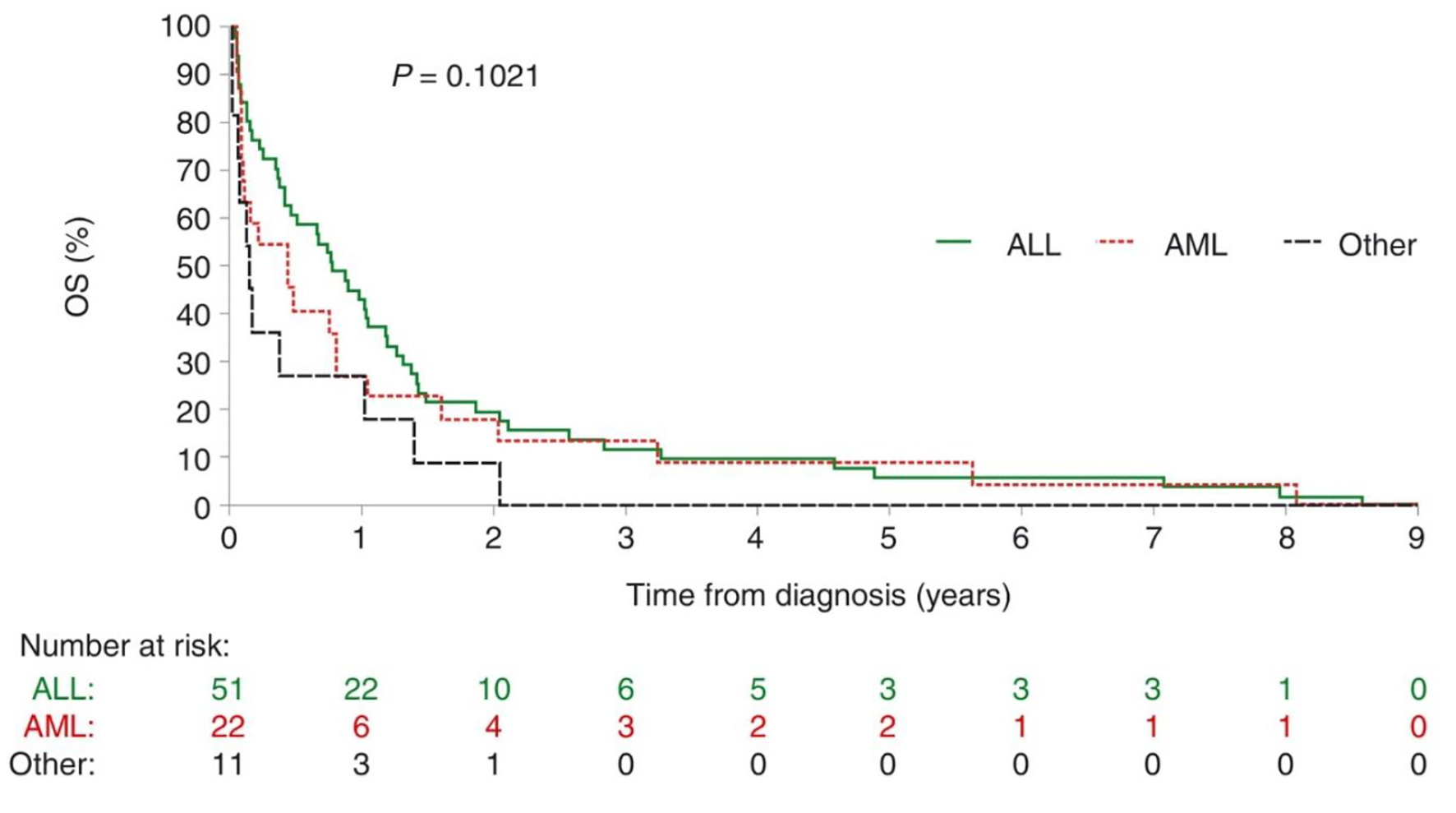
| aChemotherapy received within 45 days prior to death. AIDA: ATRA + idarubicin; ALL: acute lymphoblastic leukemia; AML: acute myeloblastic leukemia; ATRA: all-trans retinoic acid; BFM: Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster chemotherapy [11]; CALGB: Cancer and Leukemia Group B; Hyper-CVAD: hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone; IDA-FLAG: idarubicin, fludarabine, high-dose cytarabine, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; MEC: mitoxantrone, etoposide, intermediate-dose Ara-C; POMP: 6-mercaptopurine, vincristine, methotrexate, prednisone. |