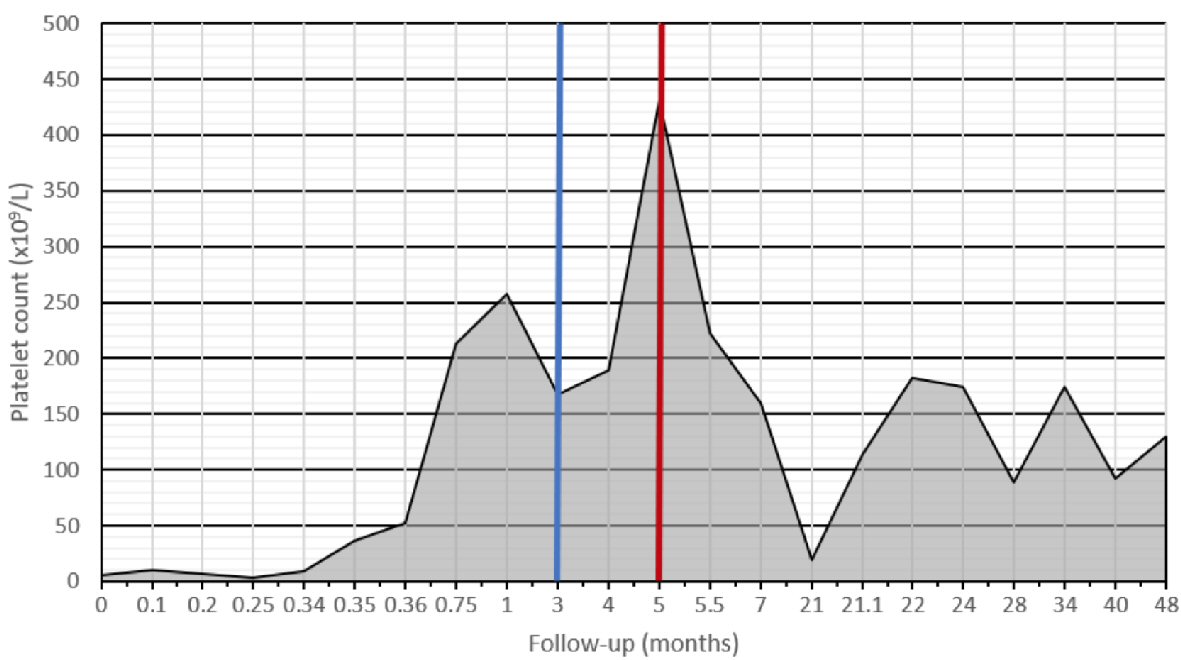
Figure 1. Platelet levels since diagnosis. Diagnosis was made at day 0. Albendazole was started at 3 months (blue line). The peak in platelet count at 5 months coincided with surgery (red line) and its associated inflammatory response. There was a period of loss to follow-up between 7 and 21 months after diagnosis. At 21 months, our patient had its first and only relapse.
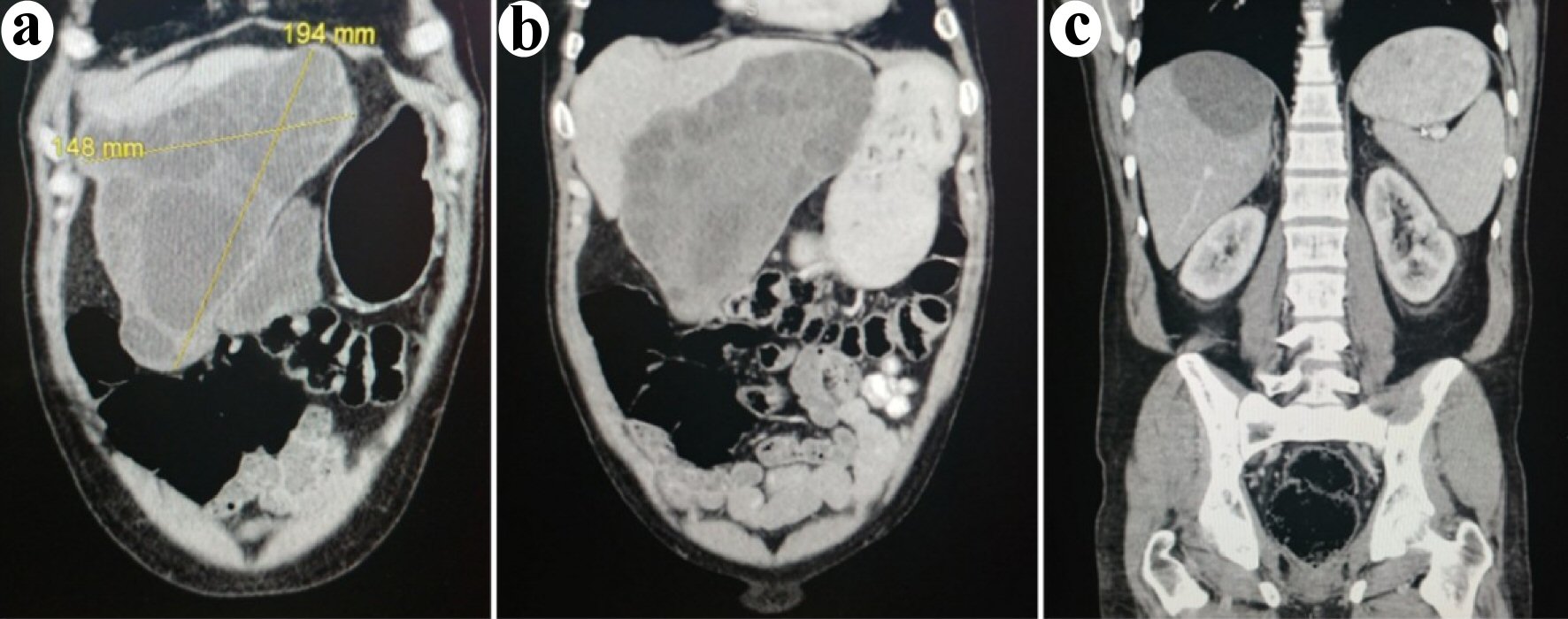
Figure 2. Coronal images of the computed tomodensitometry scan performed at presentation. (a) Anterior cut demonstrating the large left lobe cystic lesion extending downwards towards the proximal transverse colon. (b) Middle view of the abdomen demonstrating the same lesion. (c) Posterior view of the abdomen demonstrating the posterior liver lesion.
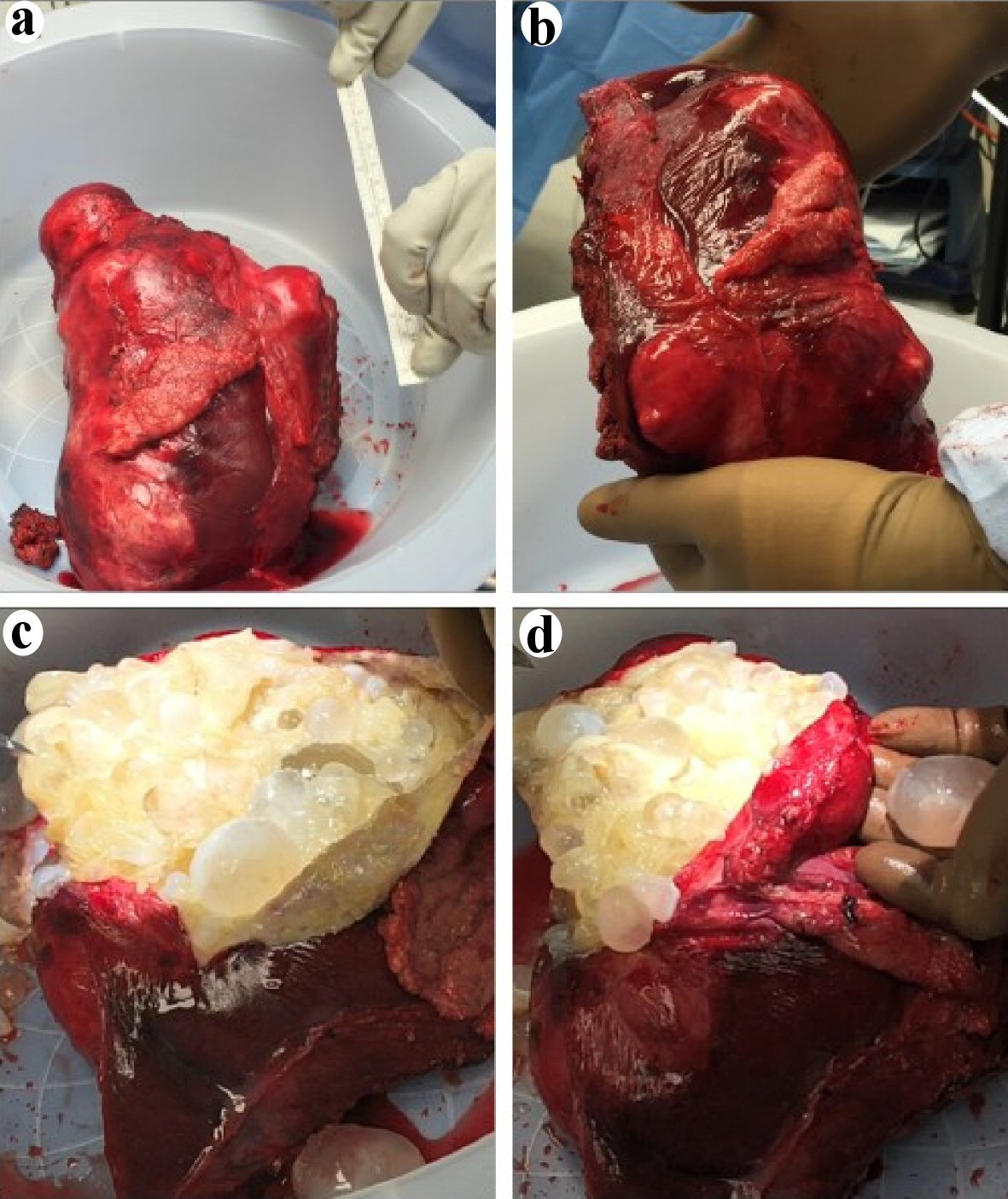
Figure 3. Postoperative partial hepatectomy specimen containing the large inferior left lobe hepatic cyst that was extending anteriorly into the abdominal fat and the proximal transverse colon. (a, b) View of the intact postoperative hepatic cyst and compared to a 15 cm (6 inches) ruler. (c, d) View of the inside of the large cyst following an excision of the cyst wall unveiling a multitude of intact smaller cysts of variable size containing a translucent fluid.


